World Resources »
Universities and Research Centers
Center for Latin American studies – Harvard University.
Stanford University Center for Latin American Studies.
Boston University Latin American Studies
Latin American Studies Association
Navigation Acts »
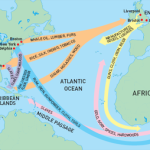
In 1660 the second Navigation Act was passed as an extension of the . During the Restoration area mercantilist economic and trade policy was widespread as it proved successful in undermining the Dutch.
In addition to the restriction of carriage of goods to and from the colonies in British owned vessels, a new provision was added by which the vessels should be manufactured in England or its colonies and the crew should consists of more than three quarters English or colonial men, but it excluded Scots. The 1660 Navigation Act added …
Townshend Acts »

Chronological events of the Townshend Acts.
Silver coins minted in the 1970’s. Historically, the burning of the Gaspee in 1772 was much removed from a reaction to the Townshend Acts of 1767.
January 1766 – New York refuses to comply with the
August 1766 – Charles Townshend assumed the position of Chancellor of the Exchequer.
June 1767 – had an overwhelming approval in parliament.
July 1767 – King George III signed the bill.
October 1767 – Boston Town Meeting under the leadership of Samuel Adams and James Ottis suggested residents and merchants to voluntarily …
Townshend Acts »

were named after Charles Townshend, the Chancellor of the Exchequer.
The acts were passed in June 1767 and were to be effective on November 20th, 1767.
The Townshend Acts consisted in a revenue measure; the New York restraining Act; the appointment of a 5 member American Board of Commissioners of Customs with headquarters in Boston; and the expansion of the Admiralty Courts to Boston, Philadelphia, Charleston in addition to the existing one in Halifax.
The imposed new tax on wine, fruits, chinaware or ceramic, white lead, painter’s colors, paper and pasteboard. …
Townshend Acts »

Trade with Great Britain had decreased from £2,378,000 to £1,634,000 by 1769. proved to be a complete failure; it did not increase revenue and confronted the population bringing them close to rebellion. Customs collections did not improve as expected because of the non importation agreement, in addition the cost of the increasing number of colonial military troops was becoming more expensive. Residents in the colonies, especially in Boston, Pennsylvania and New York were almost brought to the point of rebellion while British manufactures and merchants were having a hard …
Townshend Acts »

The 1767 Townshend Acts imposed new taxes on certain consumer products to raise revenue to pay salaries of colonial officials. It also created the American Board of Customs Commissioners and new admiralty courts to reinforce trade acts and collection of duties. In addition, the act allowed the supreme court of colonies to issue writs of assistance or search warrants on shipments to and from America.
Economic resistance
The colonists were divided over strategies of resistance and no organized opposition developed before the act went into effect on November 20th, 1767. As the …
Documents, Sugar act »

An act for granting certain duties in the British colonies and plantations in America,; for continuing, amending, and making perpetual, an act passed in the sixth year of the reign of his late majesty King George the Second, (initituled, An act for the better securing and encouraging the trade of his Majesty’s sugar colonies in America;) for applying the produce of such duties, and of the duties to arise by virtue of the said act, towards defraying the expences of defending, protecting, and securing the said colonies and plantations; for …
Documents, Molasses Act »

Whereas the Welfare and Prosperity of Your Majesty’s Sugar Colonies in America are of the greatest Consequence and Importance to the Trade, Navigation, and Strength of this Kingdom: And whereas the Planters of the said Sugar Colonies have of late Years fallen under such great Discouragements, that they are unable to improve or carry on the Sugar Trade upon an equal Footing with the Foreign Sugar Colonies, without some Advantage and Relief be given to them from Great-Britain; for Remedy whereof, and for the Good and Welfare of Your Majesty’s …
Intorelable Acts or Coercive Acts, Quartering Act »

The Quartering Act was scheduled to be modified every two years. In 1774 British parliament modified the act which was included in a package of five laws known as The purpose of these laws was to assert its power in the colony as reprisal for the Boston Tea Party protest.
By 1774 the political mood was highly charged and residents were initiating political gatherings and organizations such as the and its leaders, Samuel Adams and James Ottis, were advocating their political views.
The modified law allowed British commanders to choose where …


